Lightroom: Spot fixing with the Adjustment Brush
One of the exciting new features in Lightroom 2 is the adjustment brush which lets you to make spot fixes to your image in Lightroom. These fixes apply to only the area you select rather than the entire image. This means you can make local adjustments for contrast, saturation, exposure, brightness, clarity and sharpness without having to take the image to Photoshop to do this.
In this post I'll show you how to get started using the adjustment brush in Lightroom. 2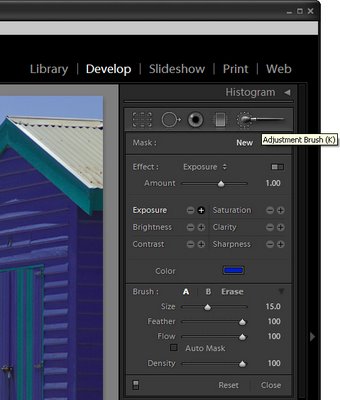
Step 1
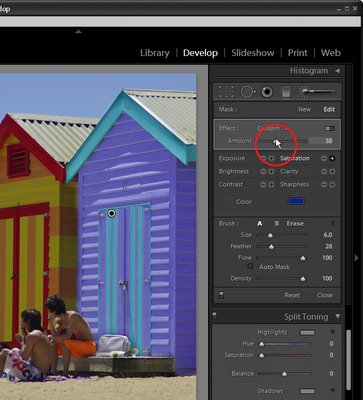
Open Lightroom and click the Develop module. Locate the Adjustment Brush and click it to select it. Hold the brush over the image to check its size. The inner circle is the hard part of the brush and the outer circle shows the edge of the feathering. To adjust the brush size use the [ and ] keys or adjust the Size and Feather using the sliders. 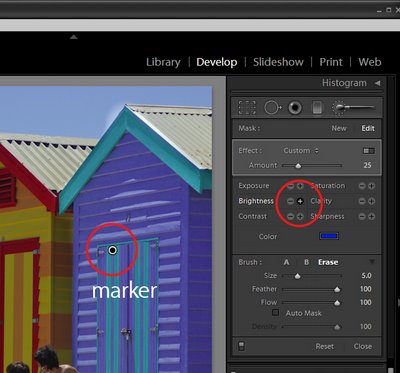
Step 2
Select the adjustment to make, such as Brightness or Saturation by clicking its + symbol to increase its value or the – symbol to decrease it. Then start painting on the image to adjust that part of the image. When you start painting the effect onto the image, Lightroom places an identifying marker on the screen. Here I have Brightness selected and the marker is visible. 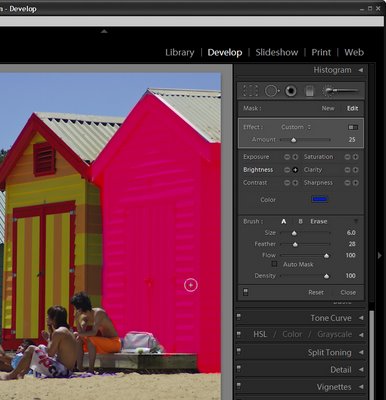
Step 3
If you don't know where you have painted – and it's often very hard to know exactly - press the O key to view or hide a mask which shows the area you have painted on. If you prefer to, you can display the mask as you work. The mask also appears if you hold your mouse over the marker.
To erase the brush strokes, click the Erase option in the brush area and erase over the area to remove the strokes. To return to painting click brush A which is the default brush and continue to paint over the area. You can also use the brush with the Alt (Option on the Mac) to remove the painted areas rather than switching between the brush and eraser. 
Step 4
If the effect is too much or too little you can adjust the intensity of the effect using the slider. 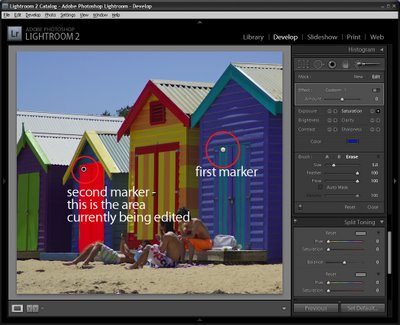
Step 5
If another area of the image requires fixing, click the New option and then repeat the steps to select a fix and then paint it onto that part of the image. Later on you can adjust either of the fixes by first clicking the Adjustment Brush tool to select it and then click on the marker for the area to change – you will see that the word Edit is now highlighted - and you can now adjust the painted area or adjust the amount of the fix.
In a future post I will look at some more advanced functions of the Adjustment Brush.
Labels: Adjustment brush, Brightness/Contrast, Lightroom 2, saturation, Sharpening