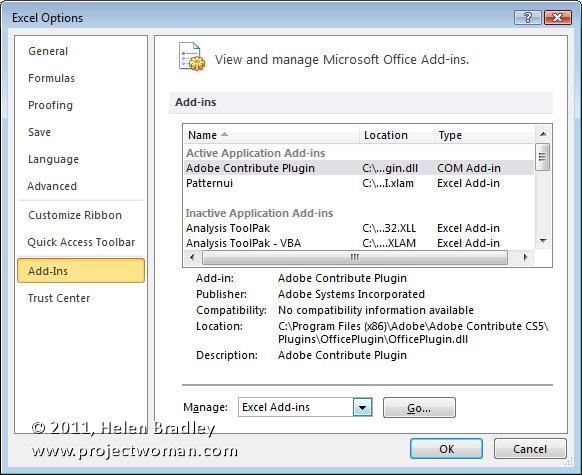
Excel 2007 & 2010 come with a number of add-ins that you can get to by choosing the Options button (File in Excel 2010) and choose Excel Options (Options in Excel 2010) and click Add-ins. From the Manage dropdown list choose Excel Add-ins and click Go.
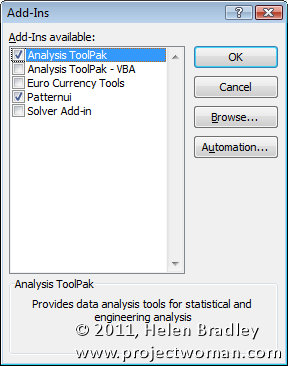
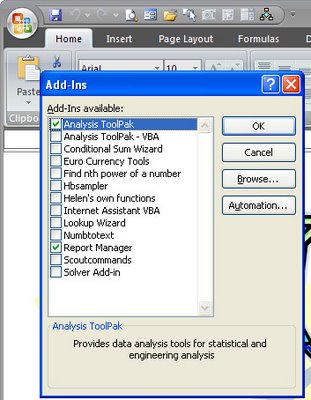
A list of available Add-ins appears in the list. Any that don’t have their checkboxes checked aren’t enabled right now.
One you might want to enable is the Analysis Toolpak – this gives you access to functions like RANDBETWEEN and NETWORKDAYS. There’s also possibly a Lookup Wizard (in Excel 2007 only – it was discontinued in Excel 2010) and a Solver add-in in the list.
Click on any of the Add-ins to add them to Excel. Once you do, they’ll be available every time you launch Excel.
RANDBETWEEN is a handy function for filling cells with a random value. It’s syntax is RANDBETWEEN(startvalue, endvalue) so to fill a range with values between 100 and 200 use =RANDBETWEEN(100,200) then copy it to the range to fill. You can read more about the function here: Random numbers in Excel.
NETWORKDAYS will calculate the number of working days between two dates. You can read more about this function here: Excel – calculating workdays with Networkdays.