Give a grunge look to a portrait using the Photoshop High Pass filter and Smart Objects – it is a quick, easy, and fully editable.
Transcript:
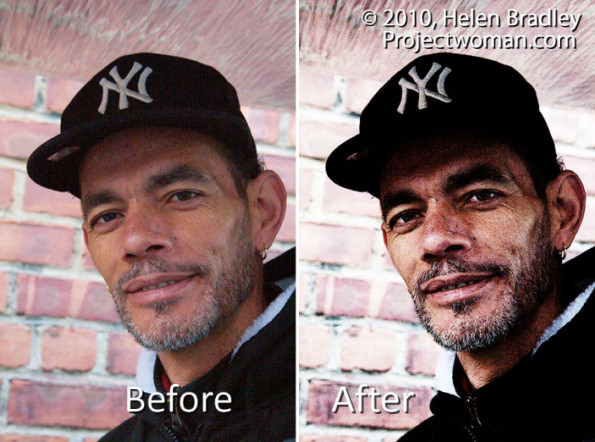
Hello, I’m Helen Bradley. Welcome to this video tutorial. In this tutorial we’re going to apply a grunge portrait effect to a portrait in Photoshop. Before we start on creating the grunge effect let’s have a look and see what we’re looking for. This is the original image that I have open here in Photoshop. All I’ve done really is cropped it. And this is the final appearance that we’re going to give this image. It’s a lot more grungy. It’s a lot darker. It’s a lot more interesting image. And the way we’re going to do it is by harnessing the power of the high pass filter which allows us to get edges out of the image. And we going to do it in a way that we could adjust it if we needed to as we go along.
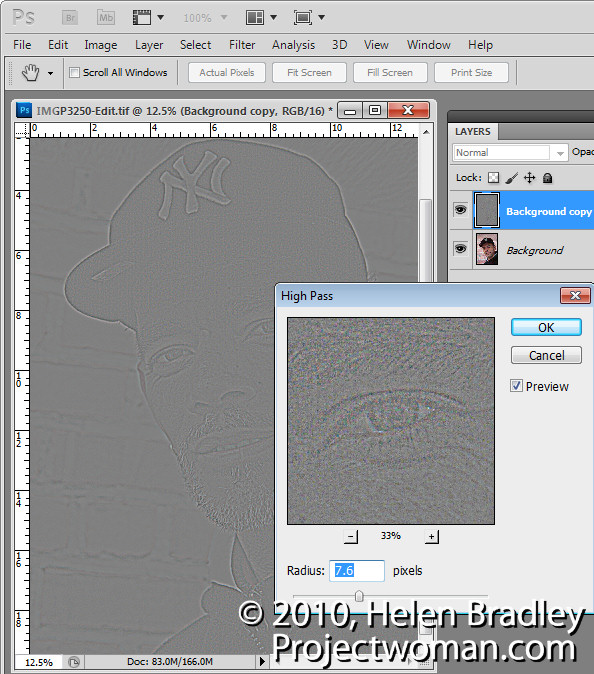
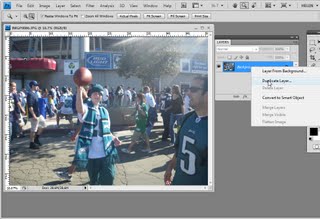
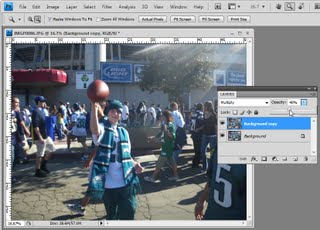
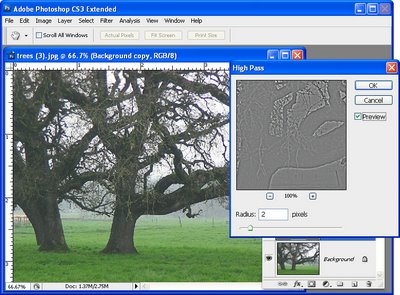
So now that we’ve seen what we’re aiming for let’s get started on our new image. And here’s the image here, and I’m just going to hide away the existing one. And we’re going to start by creating a duplicate of the background layer. I’ll right click and choose Duplicate Layer and click Ok. This is the layer that we’re going to apply the high pass filter to. And if we want it to be editable we need to first convert it for smart filters. All we’re doing effectively is making it a smart object. So we could right click and choose Convert to Smart Object, and it’s exactly the same process to choose Filter, Convert for Smart Filters. This is now a smart object so when I apply the high pass filter to it, it’s going to be done in a way that could be edited later on.
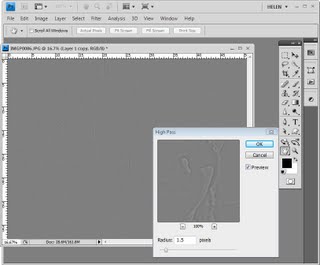
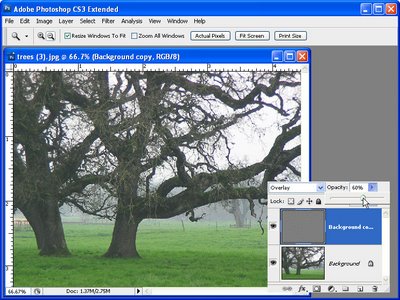
I’m choosing Filter, Other, High Pass. And with this high pass filter what I want is to begin to see the edges in the image but not a lot of color. Now depending on the sharpness of your image and exactly what the image is all about, this might be a larger or smaller value. Usually I suggest around 5 but this image is really quite soft and 5 is just not going to cut it. So I actually have this wound up to 9.6 and click Ok. But because this is a smart filler it doesn’t really matter because if it’s too much or too little we can come back later and fix it. We’re now going to set this layer blend mode to overlay so that we’re picking up these edges in the underlying image. So let’s see how far we’ve come. This is the original image and this is a slightly grittier, grainier version. But it’s going to get better.
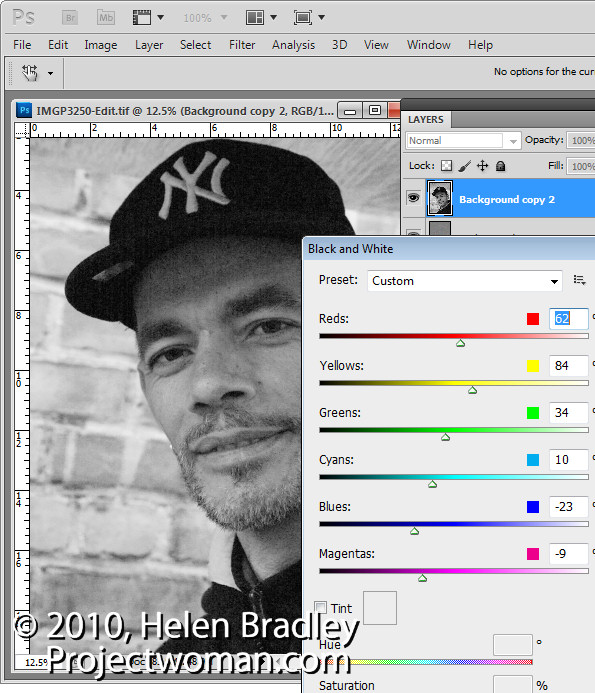
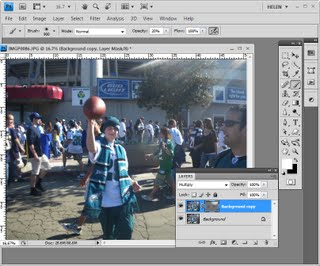
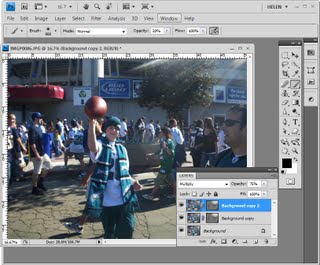
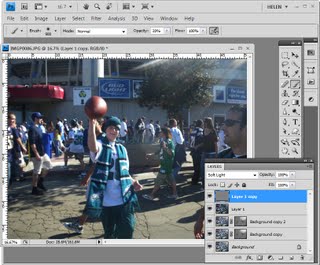
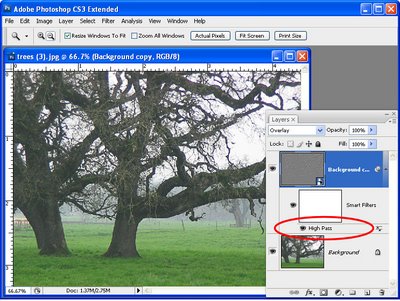
We’re going to make another duplicate of the background layer, right click and choose Duplicate Layer. And we’re going to drag this above everything else. And we’re going to make it black and white and then blend it back into the image. It’ll be easier to do if first of all we set the blend mode to something like hard light so we see the effect that we’re going to have. And I would like to do this adjustment using an adjustment layer so that we can also change that later on if we like. Let’s start with Layer, New Adjustment Layer, Black and White. I’m going to click Ok and then I’m going back into this layer stack here. And I’m going to clip this layer because right now this adjustment layer affects everything so we have a black and white image. I just want it to affect this layer. So I click on this top layer and then either position my cursor between the two layers and press the Ctrl and Alt keys, Command and Option on the Mac, to clip that or I could choose Layer and then Create Clipping Mask. It’s exactly the same thing. And what that does is it clips the effect of this black and white layer to adjust this layer underneath.
Now we can have a look at our black and white layer and see how we can grunge up this portrait a little bit better because we’re actually seeing the final results. Now we can drag on these sliders our self to make our own setting or we could select a preset. And I’m going to choose the red filter because I kind of like that effect. And I’m probably just going to lighten these red and magenta channels and perhaps even the yellow channel a little bit before I continue. So I’m just going to close that down now.
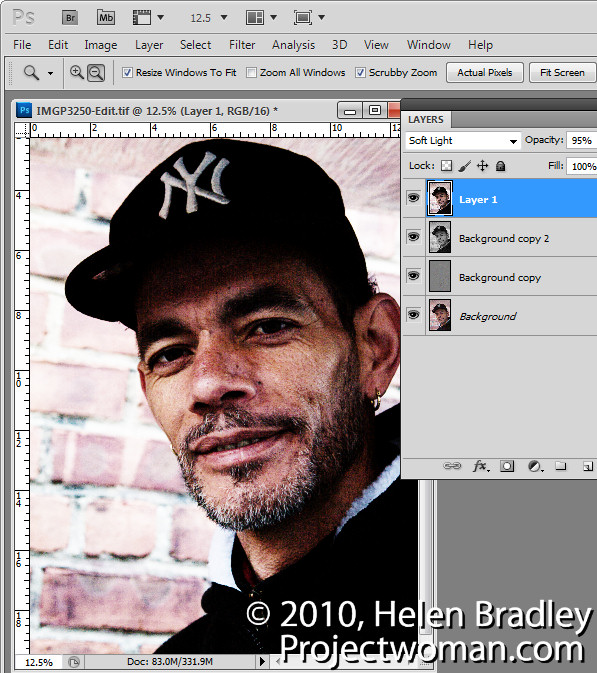
Now we’ve got the image that we want we can fine tune it by adding another adjustment to it. And for this I would use a curves adjustment. So I’m going to again choose Layer, New Adjustment Layer, Curves. And this is going to affect the entire image this curves adjustment layer. And I just really want to lighten it and add a bit more contrast into the skin tones. If I click on this slider here you can see where the skin tones are in the image. They’re in this area down here so I can drag around this area to increase the contrast in the skin tones, perhaps lighten them up a little bit as we go. And that’s really personal preference at that point.
So let’s have a look and see where we started and how far we’ve come. This is the original image. It looked a little perhaps grungy when we started but we’ve actually been able to make it even look a lot more grungy with the application of this high pass filter, blending it back in with some black and white and then adjusting the curves. Now all of these changes are adjustable so for example we can come back to this high pass filter, double click here and adjust the high pass filter effect. So we can get more or less grunge effect by just adjusting that filter. We can also come back here and adjust this black and white filter, double click here and adjust this. And the final adjustment layer was a curves adjustment layer and it’s editable too. So there’s how to create a quick and easy grunge portrait effect. It’s all editable so that you can change it and fine tune it if you like.
I’m Helen Bradley. Thank you for joining me for this YouTube video. Look out for more of my YouTube videos on this YouTube channel. I encourage you to subscribe to my channel so you’ll be advised when new videos are released. And remember to visit projectwoman.com. You’ll find more tips, tricks and techniques for working with Photoshop, Photoshop Elements and Lightroom and other applications there.