Sometimes a photo need two opposing fixes applied to different areas of the image. This poses a dilemma – if you fix one area you’ll make the other areas far worse than they started out being and vice versa. The solution is to apply both fixes but to do this using adjustment layers and to blend the results together using a mask. Here’s how to do it:
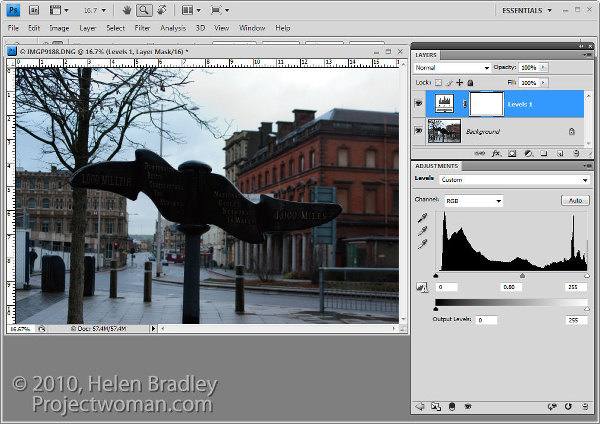
To fix the background of the image, choose Layers > New Adjustment Layer > Levels and adjust the levels to improve the contrast in the lighter areas of the image. Ignore the darker areas of the image as they are not part of this fix.
If desired, you can also adjust the saturation using Layers > New Adjustment Layer > Hue/Saturation.
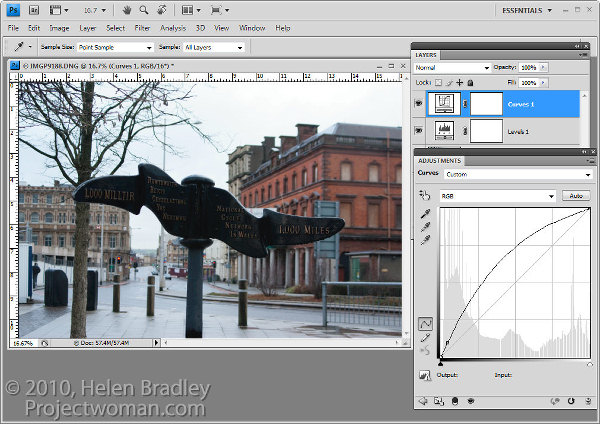
To bring detail out of the darker area in the sign you will use an additional adjustment layer. In the original blog post I used the Shadow/Highlights tool but this is one fix you cannot apply using an Adjustment Layer so you will have to use a different adjustment for this image. I will use a Curves adjustment layer here.
To do this choose Layers > New Adjustment Layer > Curves and adjust the darker end of the curve –on the left side. Drag upwards on the curve line to lighten the shadows.
If you prefer to use another tool, you can do so. However, the important thing is to fix the shadows and ignore any changes to the highlights.

The top adjustment layer contains the adjustment for the darker areas of the image and the bottom adjustment layer(s) contain the adjustment for the lighter areas of the image. To blend these layers, you will use the layer masks attached to the adjustment layers to selectively add the fixes to the image.
Unlike the adjustment layer’s Opacity slider which sets every pixel to the same opacity value, a layer mask lets you adjust the opacity selectively so one area can be 100% opaque and others can be partially or fully transparent.
For this image, as I want to lighten the sign but not anything else, it will be quickest if I start by selecting the sign on the background layer.
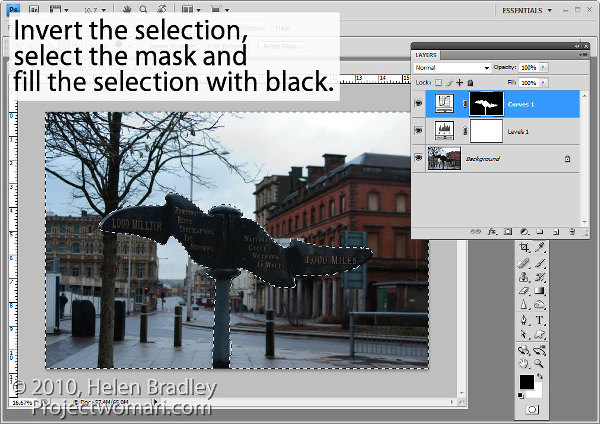
Select the mask on the Curves layer. When you are working with masks remember that “black conceals and white reveals” so painting with white on the mask reveals the adjustment on this layer and painting with black on the mask hides the adjustment.
Press Control + Shift + I (Command + Shift + I on the Mac) to invert the selection so now we have everything except the sign selected. Set the foreground color to black and press Alt + Backspace (Option + Delete on the Mac) to fill the mask except where the sign is with black.
Press Control + D (Command + D) to deselect the selection.
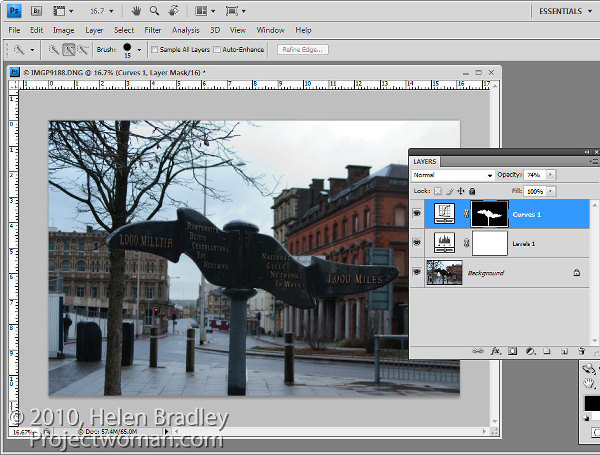
If the fix looks too intense, you can adjust the opacity of the top Curves layer down a little.
When adjusting opacity you may find it easier to judge an ideal value if you drag the Opacity slider to zero and then increase the value until you find a good fix rather than dragging it down from 100% looking for the ideal setting.
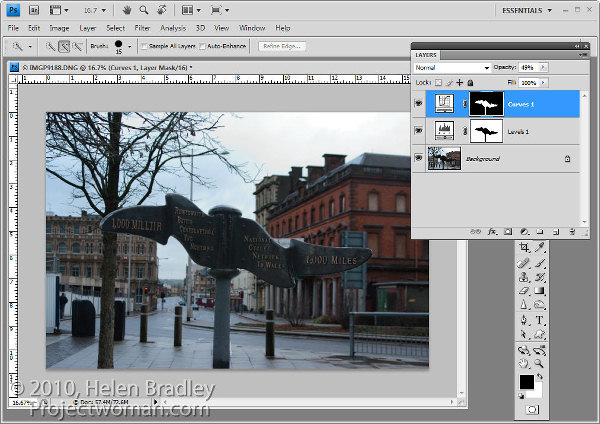
If you want to remove the sign from the Levels adjustment you can do so using an inverse of the layer mask you have already created.
To copy and invert the mask, press Alt + Shift (Option + Shift on the Mac) as you drag the mask from one adjustment layer and drop it on top of the mask on another layer. When prompted to replace the mask, answer Yes. (If you simply want to copy a mask use Control + Alt or Command + Option instead).
If you do this, you’re removing the Levels fix from the pole and you may need to adjust the Opacity of the Curves adjustment layer to compensate for this.
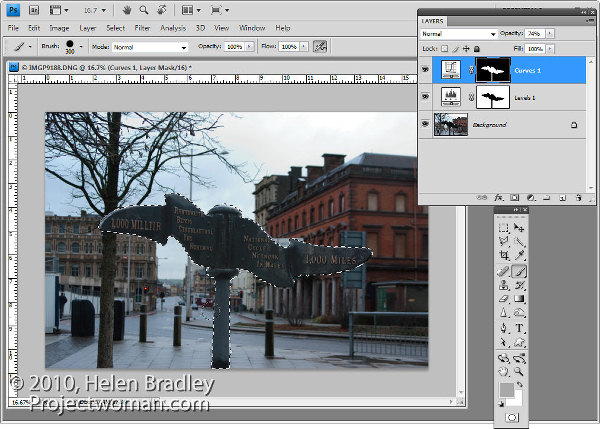
You can also adjust masks by painting on them in black, white or a shade of grey. Painting in black hides the fix on this layer, painting in white reveals the fix on this layer and painting in grey partially hides the fix.
Here I have Control + Clicked on the mask on the top Curves adjustment layer to select the white areas of the mask, then painted in grey on the mask to hide some of the lightening effect on the pole. By selecting the white area of the mask before painting I limit the paint to only the selected area which lets me work quickly.
If you go too far, switch colors and paint back the effect back.
To finish, I rotated the image to straighten the sign and cropped it to remove the distracting elements on the left side of the image.
Helen Bradley