When you’re working with Word and doing math in your tables, you need to know the name of each table cell. In a largish table it can be difficult to keep track of everything.
Back in the days of Word 97 a macro shipped with Word that would tell you the name or cell reference of a given table cell. Here’s how to take a step back in time and get that macro, install and use it, with later versions of Word:
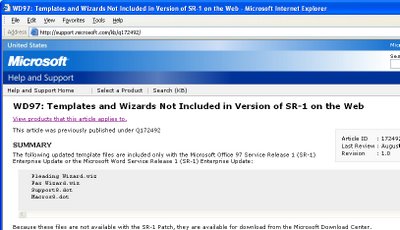
Visit http://support.microsoft.com/kb/q172492/ http://download.microsoft.com/download/word97win/addin/1.0/W9XNT4/EN-US/Wdtlupd.exe and download the file Wdtlupd.exe which is referred to on this page. This is a self-extracting zip file which includes various documents, the one we’re using is not version specific. Run this file and select a location to save the extracted files into.
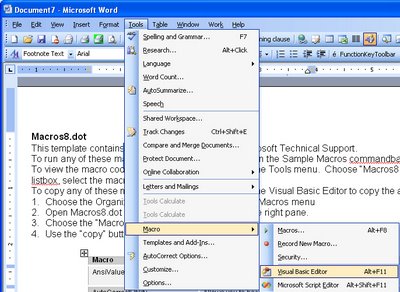
Open the folder containing the extracted files and double click the file macros8.dot to open it in your version of Word. If prompted to do so, click the Enable Macros button and the file will open automatically in Word. Now choose Tools, Macros, Visual Basic Editor if you are using Word 2003 or earlier. In Word 2007, make sure the Developer tab is visible (Office button > Word Options > Popular > Show Developer tab in the Ribbon). Choose Developer tab > Visual Basic.
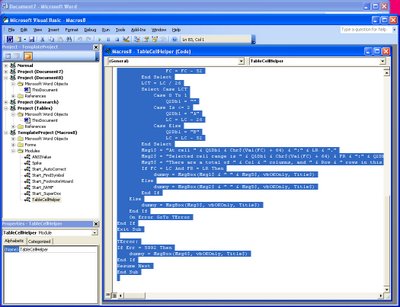
Locate the Macros8.dot file in the Project list on the left of the screen and click to open its Modules collection. Locate the module called TableCellHelper and double click it open the code window. Select the code and copy it by choosing Edit, Copy.
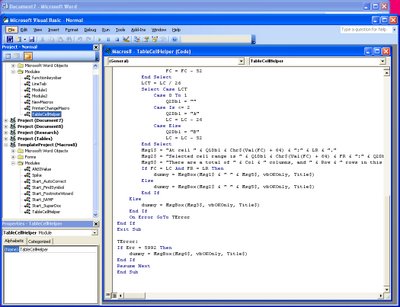
Locate the file Normal in the Project collection and click its Modules collection. Choose Insert, Module to add a new module, double click to open this new module and choose Edit, Paste to paste the copied code into the module. In the Properties area (choose View, Properties Window to display this if needed), alter the module name to TableCellHelper and, when you’re done, close the Visual Basic editor and close the file created using Macros8.dot.
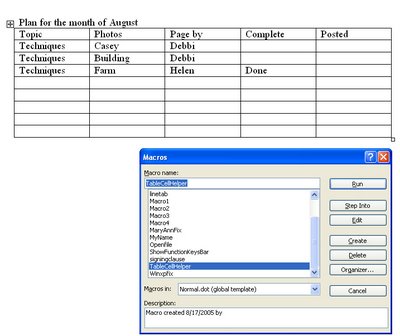
In Word 2003 and earlier, run the macro by clicking somewhere inside a table and choose Tools > Macro > Macros from the Macros in list choose Normal.dot and locate and run the macro called TableCellHelper. In Word 2007 click the Developer tab > Macros and from the Macros in list choose Normal.dotm and locate and run the macro called TableCellHelper. The macro will report the cell address and the total number of rows and columns in the table.
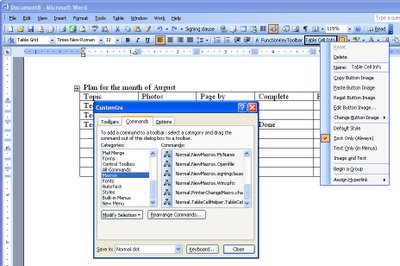
If you’d use this macro repeatedly, add it as a button to your Word 2003 (and earlier), toolbar by right clicking a toolbar and choose Customize. Click the Commands tab, select Macros from the Categories list and locate and drag the macro TableCellHelper on to the toolbar. Right click the new button and edit the name so it is shorter and more helpful. Close the Customize dialog.
- Updated 4 Oct 2017 to list a new download site for the file.








