At Halloween last year I was asked to photograph some kids I’ve shot from time to time since they were born. Basically their mum likes to have some up to date photos of the kids and Halloween seemed like as good a time as any to get some shots.
When I’m shooting like this, my aim is to get some good shots but nothing formal and I prefer not to use a flash because I get a better response from the kids without one. I captured the images in raw and I chewed through three small size camera cards in about an hour and a half.
My deal with their mum is that I get to use the photos for my work and she gets a disk of pictures. To keep this fun – so it doesn’t feel like work for me – I need a fast and effective processing workflow. I need to get the images off my camera, sorted, processed, burned to a DVD and delivered to mum in time for her to enjoy them.
Thanks to Lightroom the process was simple and, in all, I reckon I spent less than 2 hours getting the photos from the camera cards to a DVD. Here is what I call my Happy Snap Lightroom workflow – it’s what I do to quickly process casual snapshots:
Step 1: Determine a plan of attack
To begin with I have some criteria I work by. I never give away substandard photos so anything blurry, out of focus or over exposed gets permanently deleted. Then I sort out the best of the images intending to give mum around 50-60 photos of the kids – it’s a nice range of images for her to use to scrapbook and post to Facebook and it doesn’t over burden her with too many photos to choose from.
Step 2: Download the images

To begin, I download all the images from all three cards into a single folder on my hard drive (if there were only one card I would omit this step).
From there I import the images into Lightroom at the same time copying them to their permanent storage on my external photo drive and making a backup to a second drive. Copying rather than adding images to the Lightroom catalog lets me make backups and also add my metadata to the images so, when they popup on Facebook my copyright details are embedded in them.
Importing all the images in one step also means that when I’ve started the import process – which includes rendering standard previews – I can start working through the images and I don’t have to do it multiple times or switch out cards as I work – (the process works for me – your mileage may vary).
Step 3: Eliminating the duds

The first time I run through the images I am looking for images to delete as well as getting a general look at what I shot.
As I work through the images I’ll press X for images to delete and use the right arrow key to move past everything else. I’ll select to delete all out of focus images, anything where someone has their eyes closed or similar, and anything I don’t want to put my name to!
Once I’m done I choose Photo > Delete Rejected Photos to delete the images from my primary external photo drive. There are still copies on the backup drive and my hard disk but not on my main photo drive.
Step 4: Sorting the usable images

On the second run through the images I pick those I want to use. By now I have a rough idea as to what I have and what I might want to give mum. So this time I run through the images pressing P to pick an image and using the right arrow key to move past those she won’t be getting.
Step 5: Create a Collection

Once done, I isolate the picked images by clicking the first of the filter flag icons above the filmstrip. Then with only the picks visible I press Ctrl + A to select all of them and then click New Collection > Create Collection and type a name for it. Because the images are already selected, I leave the Include Selected Photos checkbox enabled and click Create.
Step 6: Apply initial processing to the images

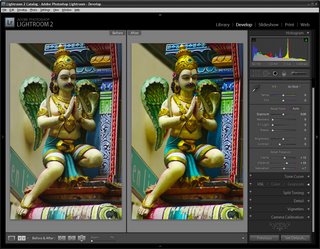
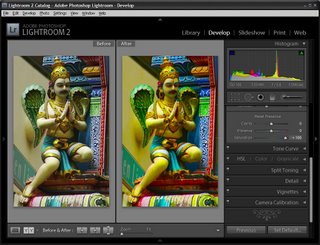
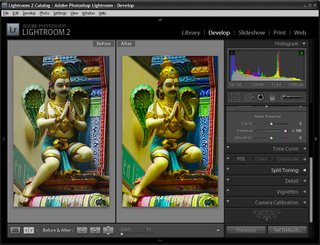
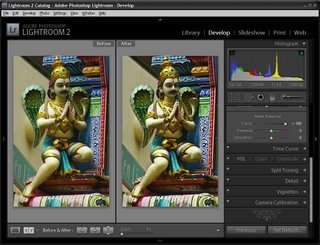
Now I have a collection of the picks and it’s time to process them. I start out by selecting all the images in Grid View in the Library and from the Quick Develop panel I select Auto Tone. This gives me a head start on fixing them but, because of the lighting, pretty much all of them needed a white balance adjustment.
Step 7: Process in the Develop module

Switching to Develop module with the filmstrip visible I selected the White Balance Selector and then made sure that Auto Dismiss was disabled. This allows me to adjust the white balance on one image and then click on the next one in the filmstrip and continue to adjust the white balance from one image to the next without having to reselect anything. Basically all that most of these images needed was some white balance adjustment.
For those that needed cropping, I cropped as I finished with white balance adjustment and then moved on to the next image. This ensured that each image was dealt with only once as I progressed across the filmstrip.
Step 8: Make one off fixes

So, having fixed the worst of the problems I work backwards through the filmstrip to see if any of the images warrant special attention. If so, I make a call to fix them or simply remove them from the collection. To remove the image, right click it and choose Remove from Collection .
Here I had one issue with a couple of images where one child’s face was in shadow. For this, I used the Adjustment Brush tool at a small size with a large feather radius. I brushed over the areas where her face was in shadow and then adjusted the Brightness and Exposure to lighten to her face. In the same images other faces were overexposed so I added a second Adjustment Brush adjustment with the opposite settings to attempt to deal with this. The final result wouldn’t stand up to close scrutiny but is just fine for the web and 6 x 4 printing.
Step 9: Export and burn

Once this was done it was time to export the images. Because they’re all in a collection, Ctrl + A selects all the images. I chose File > Export and then exported them as JPG images, 80 percent quality at the largest size and I added sharpening to them in the process. I made sure these images all went to a new folder so that they would be isolated from everything else and easy to find.
From there, it was a matter of launching Ashampoo Burning Studio, grabbing all the images and burning them to a DVD.
This workflow is one giant step better than simply burning the images direct to a DVD. It takes only a little more time with Lightroom to sort and apply some basic fixes to the images and it also means that only the best of the images get circulated and those that do have my copyright information embedded in them.
So now it’s over to you. What’s your “happy snap” workflow? Do you capture snapshots in raw? Do you process using Lightroom? And how do you get your images processed quickly so you’re not spending hours on images that are really just family snapshots?
Helen Bradley