
I was recently asked by photographer Rhonda Pierce to look at an image that she’d taken and to suggest how the background could be lightened to white in Lightroom.
This image raises an interesting question for anyone involved in postproduction and trying to understand when to use Lightroom and when to use Photoshop for editing.
Ultimately, if this image is to be printed at a large size then Lightroom really isn’t the tool for the job. There is too much wispy hair, particularly on the left side of the model’s face just opposite her mouth, which is cumbersome to work with in Lightroom. Selecting around the hair and doing a detailed job really isn’t possible or feasible in Lightroom. Ideally, Photoshop and a good extraction tool such as Vertus Fluid Mask would be the best combination to use.
However, if the image is not going to be printed at a large size and, for example, it’s destined for the web or if it is a preview image for a client where they’ll choose their favorite image from a series, then Lightroom is a good tool for the job. While Lightroom won’t do such a good job, it will do it very fast and, at the resolution we’ll be using the image we probably won’t see any real difference anyway. For this use, we can compromise on quality and harness the superior speed of Lightroom.
Later on, if this is the image the client chooses and if it will be printed at a large size, then we can wind back the Lightroom changes, export the image to Photoshop and do a proper job. We’ll only be spending time fixing those images that the client is actually paying for and that need a quality fix applied.
Lightening the background in Lightroom
So, assuming this image is destined for the web or for client preview purposes, let’s go back to the original question as to how the background can be lightened in Lightroom.
Any solution will require us to isolate the background. It’s not possible to lighten the background in Lightroom without affecting everything else in the image and that will destroy the rest of the image. The Adjustment Brush is the obvious solution.
Step 1
Click the Adjustment Brush in the Develop module and size Brush A so it is big enough to paint over the background. Add a small feather, and for this job, enable Auto mask so Lightroom will do most of the selection work for us. Set Density to 100.
Click and paint over the background with the brush. When you lift the brush you’ll see the Adjustment Pin. Make sure the cross hair in the middle of the brush stays on the background and then the Auto Mask feature will ensure that the brush doesn’t paint over anything but the background.
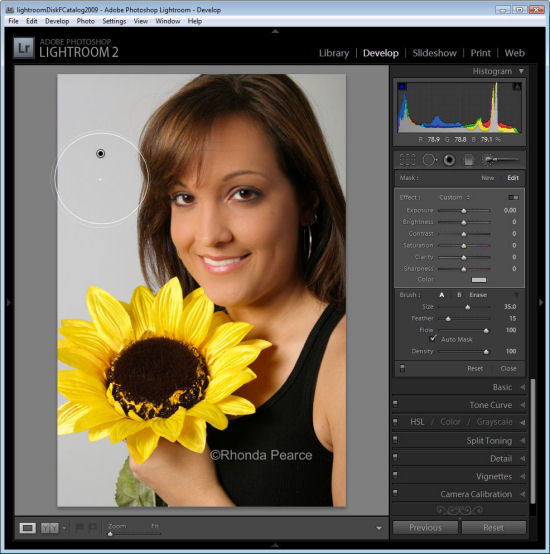
Step 2
To see the painted area, press the O key and a red overlay will appear. This makes it easier to see where you are working.
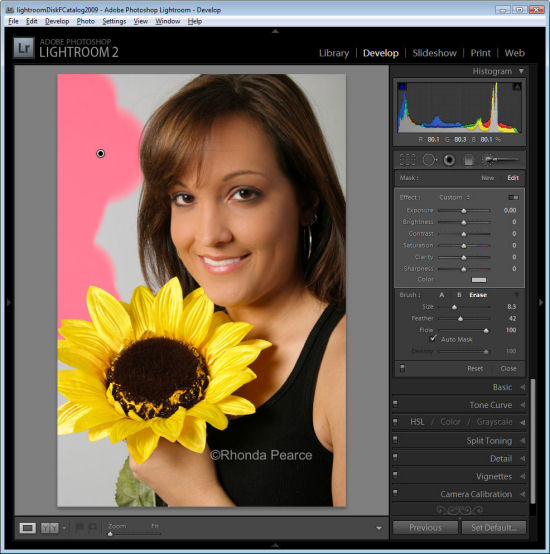
Step 3
To get the background behind the very fine hairs you might be tempted to select a very small brush and try to isolate the areas manually. However, to do the job fast, it’s more efficient to size the brush very large so the center can be positioned over an area of the background and the rest of it extends over the wispy hair area. It might help to significantly decrease the density at this point to around 30 so that you only partially select the background in the wispy hair area.
Position the brush over an area of the background so the rest of it extends over the wispy hair area and click once.

Step 4
Return to 100% density and continue to work in the other background areas making sure to avoid the wispy hair.
When the area that you want to effect are selected, press O to hide the mask.
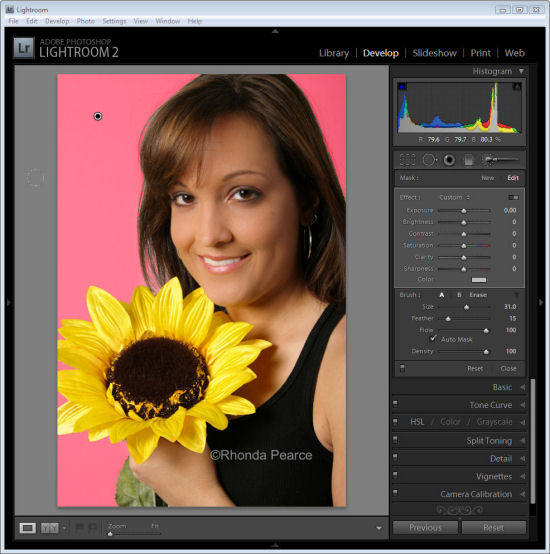
Step 5
Now adjust the settings for the Adjustment Brush. Increase the exposure and brightness until the background is white.
Click Close to close the panel and deselect the Adjustment Brush.
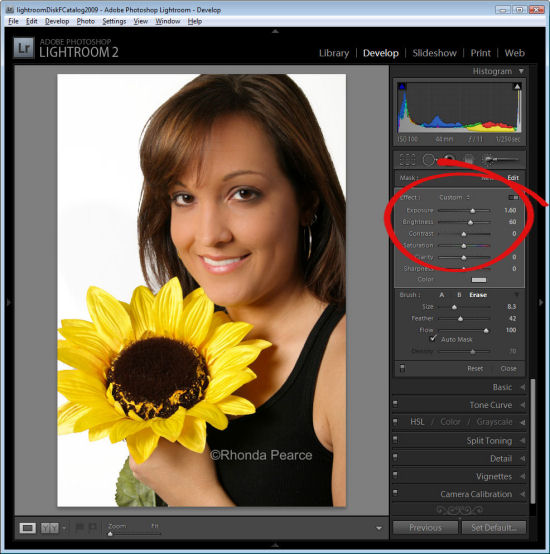
Step 6
Check the wispy hair area and you’ll see that not all the grey has gone but, when viewed in context of the remainder of the image the results are acceptable.
Press the backslash key (\) to see the image before and after the fix.

Helen Bradley

















